主动学习与交互决策过程
之前导师让调研一下“基于主动学习技术的可交互策略学习方法”,此处整理成文便于留存。
调研背景介绍
调研关键词:主动学习,可交互,策略学习,降低标注成本
相关领域
主动学习
首先我们指出广义场景下主动学习有两种含义,技术面和任务面(不冲突,侧重点不同)。 但是不论是指技术还是任务,当我们提到主动学习的时候,总是伴随着对某项成本降低的期望。
- 技术面:一种以某种原则选取数据的技术(此种含义不必须与人交互)
- 任务面:一种以某种原则选取数据从而节省监督学习标记成本的任务(标记任务需要与人交互)
策略学习
一般来说,策略是在指定任务中为完成任务目标而实行的行动准则。 目前来看,有两种被广泛使用的策略学习方法:
- 强化学习(需要与环境交互)
- 模仿学习(需要与专家系统交互)
具体调研的方向
故此调研的调研重点置于主动学习AL与强化学习RL与模仿学习IL的交叉方向上面(以降低成本为目的)。 此处的分析及本文的调研以问题为导向,不特别深入到具体技术的归类。
问题分类(调研结构以此为标准):
- 传统AL数据标记任务下的问题(监督学习中设计相关策略减少标记成本)(标记任务中与人交互)
- 使用RL/IL的policy作为AL标记任务的选取策略(AL的任务面)
- RL场景下的问题(有时与环境交互复杂昂贵)
- 定义一种数据选取的原则来指导policy的学习(AL的技术面)
- IL场景下的问题(与专家系统交互复杂昂贵)
- 定义一种数据选取的原则来指导policy的学习(AL的技术面)
另一种分类(在此调研中可找到相应模块):
- 在策略学习中无人类参与
- Active Reinforcement Learning
- 在策略学习中有人类参与
- Imitation/Reinforcement Learning in Conventional AL Process
- Interactive Reinforcement Learning
- Active Imitation Learning
三类相关方向
1. 传统AL数据标记任务
背景简介
在AL的任务面下, AL与RL有着相似的任务框架,都可以看作MDP。
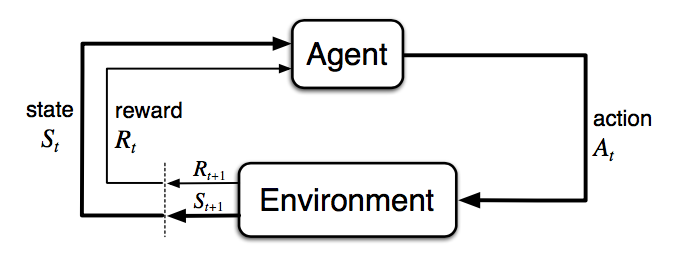
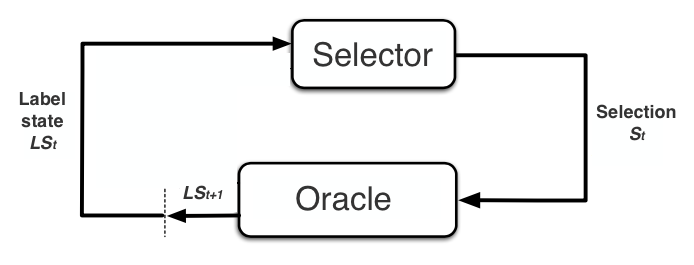
两类问题描述如下:
| RL | AL(任务面) | |
|---|---|---|
| Task | Decision tasks | Instance selection tasks with supervised learning |
| Purpose | Learn best policy to maximize the total return | Construct best labeled condition (coming with best prediction results) |
| Goal | Policy | Labeled condition |
我们将两类问题的相关概念进行对比如下:
| RL | AL(任务面) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| agent | Apply [current state => action] | selector | Apply [current labeled state => selection] |
| state | Describe current condition | labeled state | Current labeled and unlabeled data |
| action | The response from the agent under the certain state | selection | The response from the selector under the curtain labeled state. (A set of unlabeled data) |
| environment | Apply [state + action => next state + reward] | oracle/interaction | Apply [labeled state + selection => next labeled state]. Oracle annotate the selection set. |
| reward | Given by the environment after an action is taken | ||
| policy | The guideline for the agent to take optimal actions | query strategy | The guideline for the selector to make optimal selections |
| value | Evaluation of the current state/action/state-action-pair | score | Evaluation of the current potential selections |
| model (not necessary) | The learned formula of the environment | model | The learned formula of the oracle |
我们发现RL中的Policy其实对应着AL中的选取策略。 在此方向上,我们可以发现两者的区别
- 相似处:RL policy和AL strategy都应该同时考虑exploration&exploitation。
- 不同处:RL学习policy,但是AL通常使用预先启发式设定的strategy。
问题与思路
存在的问题: AL通常使用预先启发式设定的strategy其实很多时候并不是最优,而且对不同场景不一定适用。 这就带来了一个问题,这个预先设定好的heuristic有时候并不是最优,对不同场景不一定适用。
直观的方法: 从RL与AL的相似性出发,我们或许可以运用强化学习学习policy的方法来学习一个strategy。
目前主要有三类工作(数据标记任务,所以需要与人简单交互):
- 在一个相关的领域学习策略
- 之后不伴随策略在数据集间的迁移
- 之后伴随策略在数据集间的迁移
- 直接在目标领域学习策略
KEY WORDS: Learning to actively learn, Data-driven AL, Meta-active learning (ability to work with all kinds of data)
现有工作列表
在一个相关的领域学习策略,之后不伴随策略在数据集间的迁移:
- Learning active learning from data [2017, NIPS]: LAL. In pool-based AL setting. Random forest as basic classifiers. The state consist the current classifier parameters and a randomly selected data (Monte-Carlo). Train a random forest regressor that predicts the expected error reduction for a candidate sample in a particular learning state. The regressor works as the value function of the state action pair. Train the policy on the representative dataset and use it on the target dataset (without updating).
- Learning How to Actively Learn: A Deep Imitation Learning Approach [2018, Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics]: ALIL. In pool-based AL setting. The task is named entity recognition in a cross lingual setting. The state consists of the labeled and unlabelled datasets paired with the parameters of the currently trained model. An action corresponds to the selection of a query data point, and the reward function is the loss of the trained model on the hold-out evaluation set. Imitation Learning directly learns the map (policy) from state to action in a supervised manner. The policy is then used on the target dataset (without updating).
- Learning to Actively Learn: A Robust Approach [2020]: Address that previous works in this area learn a policy by optimizing with respect to data observed through prior experience (e.g., metalearning or transfer learning). This approach makes no assumptions about what parameters are likely to be encountered at test time, and therefore produces algorithms that do not suffer from a potential mismatch of priors.
在一个相关的领域学习策略,之后伴随策略在数据集间的迁移:
- Learning how to Active Learn: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach [2017, Arxiv]: PAL(Policy based Active Learning). In stream-based AL setting where the policy/strategy is to decide whether to query the current instance. The task is named entity recognition in a cross lingual setting, where transfer the learned strategy/policy to the target domain (where no enough data to learn a strategy). The policy is learned by deep Q-network. The state is the current instance the previous constructed dataset. The reward is given by a hold-out set. Then the learned policy is transferred to the target dataset with policy updating.
直接在目标领域学习策略:
- RALF: A reinforced active learning formulation for object class recognition [2012, CVPR]: First to consider AL as a MDL process. They use Q-learning to learn the adaptive combination between exploration and exploitation. Use the overall entropy as the reward in each iteration. The state is the strategy combination condition and the action is the trade-off parameter. They also used a guided initialization for Q-table.
- Active Learning by Learning [2015, AAAI]: ALBL. By Hsuan-Tien Lin (NTU). Connect AL with the well-known multi-armed bandit problem. Choose strategies in the AL process by estimating the performance of different strategies on the fly. Use EXP4.P as the core solver. The action is to choose a specific strategy.
- Learning Loss for Active Learning [2019, CVPR]: Attach a small parametric module, named “loss prediction module”, to a target network, and learn it to predict target losses of unlabeled inputs. The “loss prediction module" could be considered as the value function of the state-action pair. The state is the current model parameters and the action is the selected instance. The idea to directly predict the loss is similar to [Learning active learning from data [2017, NIPS]], but this work doesn’t need to train the policy in advance. The policy is trained during the AL process.
- Learning How to Active Learn by Dreaming [2020, ACL]: The follow-up work for [Learning How to Actively Learn: A Deep Imitation Learning Approach]. Recent data-driven AL policy learning methods are also restricted to learn from closely related domains. This method fine-tune the initial AL policy directly on the target domain of interest by using wake and dream cycles. Cross-domain and cross-lingual text classification and named entity recognition tasks. Wake learning is an AL process, and the dream learn is a policy updating process. The current weak model was used as a weak annotator to train the policy in the dream phase.
此类方法在其他类型标注任务中的相关应用:
- Multi-modal Active Learning From Human Data: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach [2019, ICMI]
- Reinforced active learning for image segmentation [2020, ICLR]
- Learning to Actively Learn Neural Machine Translation [2020, CoNLL]
- Deep Reinforcement Active Learning for Medical Image Classification [2020, MICCAI]
分析与看法
首先这一节我们面对的还是传统的AL场景,面对的主要是数据标注的任务。 相比于传统的AL启发式方法,此类学习Policy的方法对算力的要求很大,虽然标称的表现也会好,但是如果真的实际使用则需要权衡。
浅见:
- 对不同任务设计特异性的AL策略(不论是启发还是学习一个策略)是当下的趋势。
- 对于一些复杂任务,基于RL策略的迁移或许是一种良好的解决方案。
2. Reinforcement Learning 场景
背景简介
强化学习相关知识与概念在此不赘述。 具体可以参见这篇文章。
强化学习面对的问题场景就是一个广义的学习一个智能 agent 的场景。 一般通过与环境的交互来学习 agent 的 policy。 环境交互的过程中一般会黑盒地出状态的转移以及相应的奖励。 Policy 的训练依赖于观测的结果。 一般是在观测到的 trajectory 中进行训练: $${S_0,A_0,R_0,S_1,A_1,R_1,S_2,A_2,R_2,…,S_{n-1},A_{n-1},R_{n-1},S_n,R_n}$$ (主流的强化学习方法分为 model-based 与 model-free 两种,区别在 policy 的训练是否依赖对环境的状态转移建模。)
训练的过程中存在一个问题:若持续以当前的学到的策略与环境进行交互(exploitation),那么学习的结果则容易陷入一个局部最优当中。 所以在强化学习中 exploitation 需要伴随 exploration,这样可以避免陷入局部最优并且找到更好的策略。 最简单的分配方式是 ,按照一定比例分配 exploitation 和 exploration。 如果 exploitation 过多,则容易陷入局部最优,如果 exploration 过多,则较难有充足的数据训练一个较好的policy。 所以说 exploitation 之外的 exploration 也十分重要。
通常情况下RL假设与环境的交互是即时完成且没有花费的。 然而现实情况下,与环境的交互,通常是需要付出代价的(时间或算力或实际成本)。 在 large, high-dimensional environment 中,这个成本更为高昂(复杂的模拟计算等)。 此时我们希望我们每一次的交互都能被更好的利用起来:
- 在 exploitation 中用更好的训练方式(大部分强化学习在研究的的)
- 在 exploration 中选择更好的交互样本,更高效探索(active)
于是RL则与AL选取更优样本的逻辑产生了交叉,主要是聚焦于探索的场景下。 《人工智能:一种现代的方法》21.3中的主动强化学习提到了这一现象。 我们想更优更高效地 exploration(Agent 不必关心那些它知道不需要的而且可以避开的状态的具体效用)。 此处我们称这种选取为 active reinforcement learning。
此处的 Active 不一定一定要有人的存在。 这里的 Active 含义: the agent seeks out novelty based on its own “internal” estimate of what action sequences will lead to interesting transitions.
问题与思路
存在的问题: RL与环境交互会产生交互成本。 较多的探索会影响模型的训练,同时也会造成一定的cost损失。
直观的方法: 借鉴AL的思路,制定或学习探索的方式,更高效的探索,使相同数量的探索下训练的policy更好。
目前主要有以下几类工作:
- ARL: 整体框架仍是RL的框架。加入探索的heuristic。(不与人交互,只与环境交互)
- ARL-1: 与环境交互获取状态转移和奖励时产生cost
- ARL_2: 只在与环境交互获取奖励时产生cost,状态转移不产生cost。
- IRL: 以RL的框架为基础,添加interactive的部分。(需要与人交互)
KEY WORDS: active exploration, active reinforcement learning, interactive reinforcement learning
现有工作
ARL-1:与环境交互获取状态转移和奖励时产生cost。(No human interactions)
由于需要主动的选择来与环境进行交互,一般来说是要选取我们认为环境能反馈更多信息的样例。 通常的做法是在对环境的建模上来衡量informativeness。 具体衡量的方法与AL中的方法相似(QBC/Entropy/Information Gain, etc.) 所以说绝大部分的工作都是基于Model-based RL。
- Active Reinforcement Learning [ICML, 2008]: Before this work, many ideas are trying to explore the actions which agents has experienced the fewest number of times in the past. In this paper, the agent determines the sensitivity of the optimal policy to changes in transitions and rewards. It then focuses its exploration on the regions of space to which the optimal policy is most sensitive. The process is similar to ADP. Use Taylor’s approximation to model the local sensitivity of the utility on current policy.
- VIME: Variational Information Maximizing Exploration [2016, NIPS]: Agent should take actions that maximize the reduction in uncertainty about the dynamics (transition). Use BNN to learn the model. This can be formalized as maximizing the sum of reductions in entropy of transition probability. The exploration to the uncertain state of the models should reward more.
- Model-based active exploration [2019, ICML]: Better state-action pair makes the model ensemble changes more. The utility of the state action pair is the disagreement among the next-state distributions given s and a, in terms of JSD (Jensen-Shannon Divergence), of all possible transition functions weighted by their probability. (用可能的transaction分布变化作为criteria。)
- Self-supervised exploration via disagreement [2019, ICML]: The idea is similar to Model-based active exploration. Generate an intrinsic reward, defined as some difference measure (i.e., KL-divergence, total variation) across the output of different models in the ensemble drives exploration. (Such exploration might be ineffective, as the policy may visit regions of the state space which have no relation to solving the task.)
- Explicit explore-exploit algorithms in continuous state spaces [2019, NIPS]: Applicable in large or infinite state spaces. Exploration and exploitation are controlled by a threshold. Exploration is guided by the disagreement in the model set. And the models updated after get the exploration trajectories. Exploitation is guided by one of the model in the model set.
- Ready Policy One: World Building Through Active Learning [2020, Arxiv]: View MBRL exploration as an active learning problem (select trajectory from trajectory space), where we aim to improve the world model in the fewest samples possible. Acquiring data that most likely leads to subsequent improvement in the model. The exploration metric is based on reward variance computed from a (finite) collection of models.
- SAMBA: Safe Model-Based & Active Reinforcement Learning [2020, Arxiv]: From Huawei UK. Safe-RL setting, every trajectory comes with a cost. Aim at minimizing cost, maximizing active exploration (bi-objective), and meeting safety constraints. Increases in regions with dense training-data (due to the usage of CVaR constraint) to aid agents in exploring novel yet safe tuples. The exploration use an expected leave-one-out semi-metric between two Gaussian processes defined, for a one query state-action pair. (Model change)
ARL-2:只在与环境交互获取奖励时产生cost,状态转移不产生cost。
Specify the cost C:
- Active reinforcement learning with monte-carlo tree search [2018]: The reward needs to be paid to observe. The received reward has the discount for the querying cost.
- Active Measure Reinforcement Learning for Observation Cost Minimization [2020]: The policy applied with Q-learning. Add whether to query as part of the action in Q-table, so the number of action would be twice as large as the ordinary Q-table. After each query, it jump to the queried state and update a transition model. Otherwise, it go to the state according to the transition model. (没太懂这篇文章的intuition)
IRL:与环境交互获取状态转移和奖励时产生cost,人类交互不产生cost
此类问题的背景仍旧是搜索空间大,搜索耗时且复杂。 所以仍然是在与环境交互时产生cost,希望使用人类专家在训练时的介入来缓解这个问题。 人类专家的交互仍然是为了使exploration更高效。 但是需要强调,此处的问题并没有对与人类专家交互的数量与质量进行假设。
- Exploration from Demonstration for Interactive Reinforcement Learning [2016, aamas]: A model-free policy-based approach, uses human demonstrations to guide search space exploration. The demonstrations are used to learn an exploration policy that actively guides the agent towards important aspects of the problem. In the proceeding of a episode, when the agent reaches a informative state (computed by leverage and discrepancy), it queries the action from the state with the closest leverage to the current state, then update the policy parameters. A self-play with the environment followed in this episode, and the parameters are keep updating.
- Interactive Teaching Strategies for Agent Training [2016]: A work by Microsoft. Include two agent: student(learn from RL) and teacher(fixed human policy). Contains two module: student initiated and teacher initiated. Query when the student has a low Q-value difference on the current state. (the student is uncertain about which action to take)
- Agent-Agnostic Human-in-the-Loop Reinforcement Learning [2016, NIPS]: Develop a framework for human-agent interaction that is agent-agnostic and can capture a wide range of ways a human can help an RL agent (e.g. Q-values, action optimality, or the true reward.)
分析与看法
ARL和普通RL的工作界限其实并不是很明显,因为很多 RL 的工作也是需要处理 exploitation 和 exploration。 此处只是挑了一些很明显使用到 AL 相关思路的文章,如果要详尽调研则较为困难。
IRL 其实比较有趣,它主要是想通过人的参与让与环境的交互更高效,人在这里只是起到画龙点睛的作用,或许这种交互可以用到很多 RL 系统。
3. Imitation Learning 场景
背景简介
模仿学习相关知识与概念在此不赘述。 具体可以参见这篇文章。
简单来说,模仿学习会在学习的过程中与专家交互,同时获得专家对指定 state 所作出的 action $$\pi_*(s)$$。 模仿学习的目标为学习一个 policy,使其与专家的 policy 尽可能接近(模型生成的状态-动作轨迹分布和输入的轨迹分布相匹配/获得同样的 reward 等)。
通常情况下,根据应用场景的不同,IL可以分为以下几类(By ICML 2018 IL Tutorial):
- Behavior cloning
- Direct policy learning (multiple step BC)
- Inverse reinforcement learning (assume learning R is statistically easier)
与RL类似,IL同样是在观测到的trajectory中进行训练: $${S_0,A_0,S_1,A_1,S_2,A_2,…,S_{n-1},A_{n-1},S_n}$$。 不同的是,在 trajectory 中并没有每一步的 reward。
问题与思路
存在的问题: 当我们想要通过模仿来学习策略的时候,唯一的学习来源来自于 Expert 对所询问的 stat e的回答(相应 action)。 这种与 Expert 的交互是昂贵的。
直观的方法: 询问专家时,挑选更有价值的 state 来询问相应的 action。
目前的工作也是基于 IL 的分类,存在于以下两类:
- Direct Policy Learning
- Inverse reinforcement learning
在 IL 中,一部分工作使用一定数量与专家交互下 policy 的表现作为评估,类似于 AL 中的学习曲线。 所以说一部分 IL 天然的可以看作 AL 的问题(以 AL 选取策略降低与专家交互成本)。 (另一部分使用一定数量与环境交互下 policy 的表现作为评估,是以人的参与降低与环境交互成本,类似之前提到的 IRL。)
KEY WORDS: imitation learning, active imitation learning, active inverse reinforcement learning
现有工作
Under Direct Policy Learning:
此类工作的目标是学一个 state 到 action 的 map,是一个监督学习的过程,选取的方式基于学习到的 supervised model。
- Active Imitation Learning: Formal and Practical Reductions to I.I.D. Learning [2014, JMLR]: Under the subclass Direct Policy Learning. Construct a committee by bootstrap sampling (posterior over policies). Select states by density weighted QBC strategy and get the corresponding action. The density is from trajectory from the simulated environment. Maintain a supervised labeled state-action pairs.
- Query-Efficient Imitation Learning for End-to-End Simulated Driving [2017, AAAI]: Maintain a safety classifier to decide which state needs to be queried. Use supervised loss between the action given by trained policy and reference policy on the visited states.
Under Inverse reinforcement learning:
由于目标之一是学习 value function,所以通常是以当前的 value function 来构建选取 state 的逻辑。
- Active Learning for Reward Estimation in Inverse Reinforcement Learning [2009, ECML PKDD]: Take the entropy of the value prediction on the state as the sample strategy (where the reward is unsure). i.e. the disagreement on the learned reward functions. It query the specific action from the oracle on the selected state. (162)
- Where to Add Actions in Human-in-the-Loop Reinforcement Learning [2017, AAAI]: Selecting the state s to query the action where adding the next action most improves the estimated value of state.
- Policy Optimization with Demonstrations [2018, ICML]: Use discriminator between human demonstrations and trajectory from environment to make the exploration close to the human’s action. The purpose is to use the current demonstration to train a policy as good as possible. (Demonstration is collected in loops, could be considered as an AL process.)
- Interactive Teaching Algorithms for Inverse Reinforcement Learning [2019, IJCAI]: Focus on how could a teacher provide an informative sequence of demonstrations to an IRL learner to speed up the learning process. The main idea is to pick a demonstration with maximal discrepancy between the learner’s current policy and the teacher’s policy in terms of expected reward.
分析与看法
Imitation Learning 天然和 AL 有很多相似的地方。 AL 是想模仿 oracle 的黑盒模型,IL 是想模仿 expert 的黑盒策略。 人在 IL 中的重要程度就像人在 AL 中的重要程度一样,因为人类是系统唯一可以获得监督信息的地方。 所以说本节所在意的并不是环境的交互成本,而是人类的交互成本,这就使 AIL 与 IRL 产生了区别(问题的定义不同)。
总结
本文以两种维度介绍了主动学习与可交互策略相关的问题,并以第一种维度进行了展开(第二种维度同样可以找到相应模块)。
其中对于人类专家存在的交互式的策略学习,当前已经有了一些综述或者前瞻的文章。 这些工作主要介绍了不同交互的方式与目的,并不一定包含减少标记成本的模块。
- Power to the people: The role of humans in interactive machine learning [2014, AI Magazine]
- Scalable agent alignment via reward modeling: a research direction [2018]: From Deepmind.
- Leveraging Human Guidance for Deep Reinforcement Learning Tasks [2019, IJCAI]
- A Survey on Interactive Reinforcement Learning: Design Principles and Open Challenges [2020, ACM DIS]
最新进展&发展趋势
本文并未对相关技术的最新进展展开探讨,但是从问题的角度来讲的确出现了一些新问题。 包括但不限于:
- 由 active RL 到 active safe RL
- IRL 中考虑交互的方式(不同形式的指导,或者相同形式指导的不同展现方式)
但是现在来看问题的大类并没有发生什么改变。 交互的成本只有两类:与环境交互成本,与人类专家交互成本。 在这次简要的调查中并没有发现其他类的问题。